Mastering Wheat Weevil Control: Essential Strategies for Farmers

The agricultural industry faces numerous challenges, and one of the most significant threats to wheat production is the wheat weevil. This small but notorious pest can devastate entire harvests if not properly managed. In this guide, we will explore the various aspects of wheat weevil control, offering comprehensive strategies to ensure your grain remains healthy and safe. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to combat these pests effectively and maintain the quality of your crops.
Understanding the Wheat Weevil
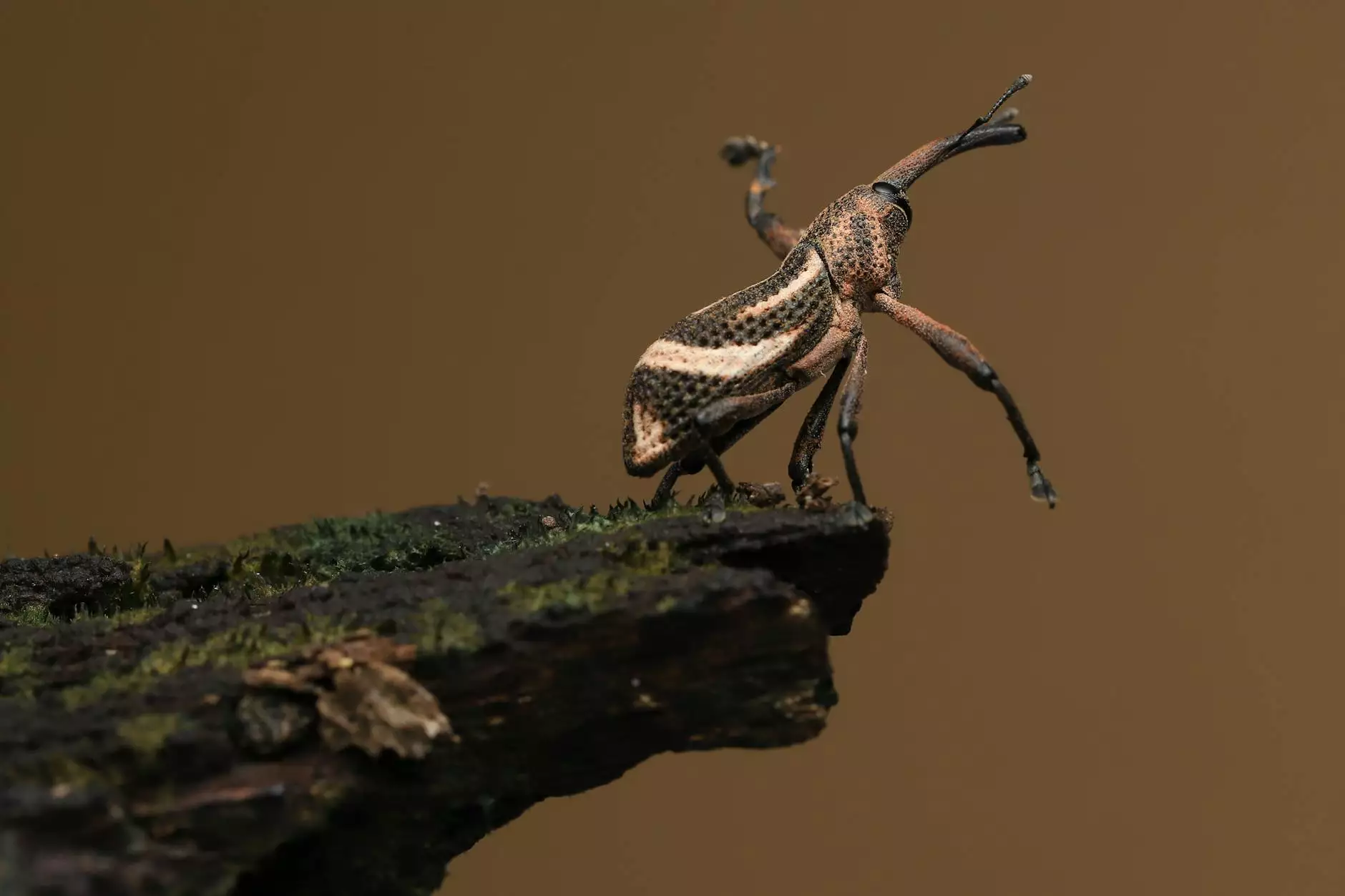
The wheat weevil (Sitophilus granarius) is a behaviorally and biologically fascinating pest that is a member of the beetle family. Its life cycle and habits make it particularly troublesome for farmers. Here’s what you need to know:
- Physical Description: Adult wheat weevils are typically 3-4 mm in length, with elongated bodies and a distinctive long snout that they use to bore into grains.
- Life Cycle: The lifecycle of the wheat weevil includes an egg, larva, pupa, and adult stage, occurring within the grain, which makes it difficult to control.
- Feeding Habits: The larvae feed on the interior of grains, making their control even more urgent.
Why Wheat Weevil Control is Crucial
Effective wheat weevil control is essential for several reasons:
- Economic Impact: Infestations can lead to significant financial losses, reducing the quality and quantity of your harvest.
- Food Safety: Contaminated grain can pose health risks to consumers.
- Market Reputation: Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for market competitiveness.
Preventive Measures for Wheat Weevil Control
Prevention is the first line of defense against wheat weevils. Implementing effective measures can significantly reduce the risk of an infestation:
1. Sanitation Practices
Maintaining cleanliness in storage facilities and equipment plays a crucial role in prevention.
- Regularly clean storage areas to eliminate dust, grain residues, and potential breeding grounds.
- Seal all openings in storage facilities to prevent weevils from entering.
2. Inspection of Grains
Vigilantly inspecting grain for signs of pests can help catch infestations early. Look for:
- Small holes in the grain, indicating weevil entry.
- Surface damage and frass (insect droppings) in stored grains.
3. Grain Treatment
Treating grains before storage can drastically reduce the risk of infestations. Options include:
- Insecticides: Using appropriate insecticides can help eliminate existing infestations.
- Heat Treatment: Exposing grain to high temperatures can kill weevil eggs and larvae.
Detecting Wheat Weevil Infestations
Early detection is vital for effective wheat weevil control. Farmers should be familiar with the signs of infestation:
Visual Inspection
Regular checks of stored grain are essential. Use the following methods for effective monitoring:
- Check for physical signs of damage, such as holes and dust in grain storage.
- Use pheromone traps to monitor adult weevil activity.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling is an invaluable practice in pest management:
- Take samples from different locations within the storage to assess the infestation level.
- Evaluate the samples for live insects, damage, and overall grain quality.
Wheat Weevil Control Methods
When an infestation is confirmed, swift action is necessary. Below are some of the most effective wheat weevil control methodologies:
1. Chemical Control
Chemicals can be a potent solution, but they should be used responsibly:
- Choose targeted insecticides specific to the wheat weevil.
- Follow all label instructions carefully to ensure safety and effectiveness.
2. Biological Control
Consider using natural predators to manage weevil populations:
- Introduce Trichogramma wasps, which can parasitize weevil eggs.
- Maintain beneficial insect populations that can aid in controlling weevil numbers.
3. Mechanical Control Options
For a more hands-on approach, mechanical methods can assist in management:
- Vacuuming grain storage areas to physically remove weevils and their residues.
- Using heat to combat infestations in smaller storage units.
Post-Control Strategies
Once the infestation is under control, it is vital to implement measures to prevent recurrences:
1. Continuous Monitoring
Monitor grain regularly for any signs of new infestations. The use of traps and visual inspections should continue as a preventive measure.
2. Seasonal Practices
Implement seasonal controls and inspections as a routine part of your farming operations:
- Rotate grain storage locations to minimize weevil establishment.
- Incorporate frequent cleaning and inspections in all agricultural practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective wheat weevil control is crucial for maintaining high-quality wheat production. By adopting a proactive approach that includes preventative measures, regular inspections, and a robust response strategy, farmers can protect their livelihoods and ensure the success of their wheat crops. Remember, understanding your enemy is the first step in defeating it. Stay informed, take action, and achieve the success your farming operation deserves!
FAQs on Wheat Weevil Control
1. How do I know if my stored grain is infested?
Look for visual signs such as small holes in grains, frass, or any unusual dust patterns in your storage area.
2. Are there natural methods to control wheat weevils?
Yes, biological control methods can be effective, including the introduction of natural predators.
3. How often should I inspect my grain?
Regular inspections are recommended, ideally at least once a month or more frequently during peak pest seasons.
4. Can wheat weevils contaminate my grain?
Yes, infested grain can become contaminated, affecting both quality and safety.
5. What should I do if I find a significant infestation?
Act quickly by isolating the affected grain, using appropriate insecticides, and consulting pest management professionals if necessary.